Arrays
An antenna array (or array antenna) is, much like it sounds, several elements interconnected and arranged in a regular structure to form an individual antenna. The purpose of an array is to produce radiation patterns that have certain desirable characteristics that a single element would not. A stacked dipole array, as shown in figure 21, is comprised of vertical dipole elements. This dipole array has an omnidirectional pattern like the element dipole does; but has higher gain and a narrower main lobe beamwidth in the vertical plane. Figure 22 shows how the vertical-plane gain of the dipole element can be “enhanced” by making an array of them. Figure 22(a) represents the radiation pattern of one element. Figure 22(b) is the pattern of two elements, and figure 22(c) is for three elements.
Figure 21. A typical vertical array using folded dipoles
Figure 22. Vertical-plane radiation patterns for (a) single half-wave dipole, (b) two-element array, and (c) threeelement array
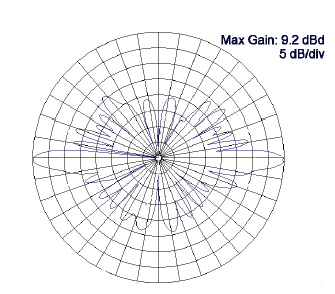
This is called a binomial or collinear array [14]. As the number of elements is increased, the gain increases and the beamwidth decreases. The omnidirectional coaxial collinear antenna (often referred to as an “omni”) is a very popular array design for base stations. It is comprised of quarter-wave coaxial sections with inner and outer conductors transposed at each junction. A conceptual illustration is shown in figure 23. Although more complex than the illustration, this antenna array behaves like a series of vertical dipoles stacked one above the other. The more stacked sections, the greater the gain and the narrower the vertical beamwidth. A vertical-plane pattern for this type of antenna is shown in figure 24. Variations in electrical design can produce a downward tilt of the vertical-plane pattern as shown in figure 25. This antenna often is enclosed in a fiberglass sheath, called a radome, and appears as a simple pole that can be mounted off the side or on top of a mast or tower.
Figure 23. A coaxial collinear array
As with all antennas, the array is frequencydependent. The gain, directivity, and radiation pattern are each a function of frequency. Some antennas will work well only for the design frequency, and their performance will degrade as the operating frequency is separated from the design frequency.


Comments
Post a Comment